We use cookies on this site to enhance your user experience
By clicking the Accept button, you agree to us doing so. More info on our cookie policy
We use cookies on this site to enhance your user experience
By clicking the Accept button, you agree to us doing so. More info on our cookie policy
Published: Sep 1, 2025
Authors:
Xiaochan (Luna) Xue
,
Shucheng Yu
,
Saurabh Parkar
,
Yao Zheng
O-RAN/AI-RAN Series
This post is part of a series all about O-RAN/AI-RAN.
Fundamental
Advanced
NextG UAV Detection Using an O-RAN-Controlled Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS)
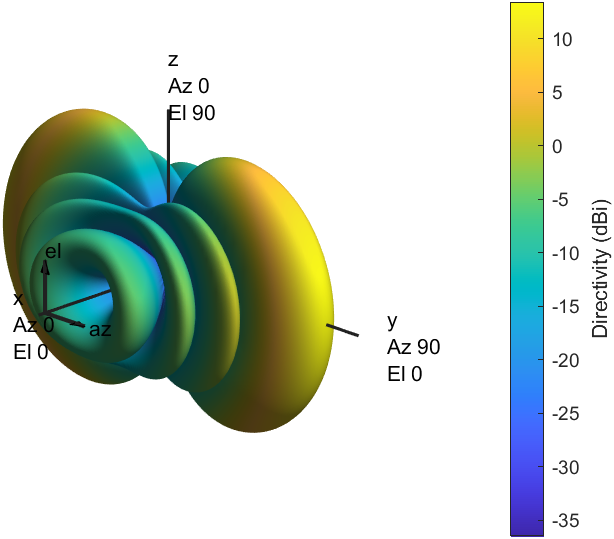
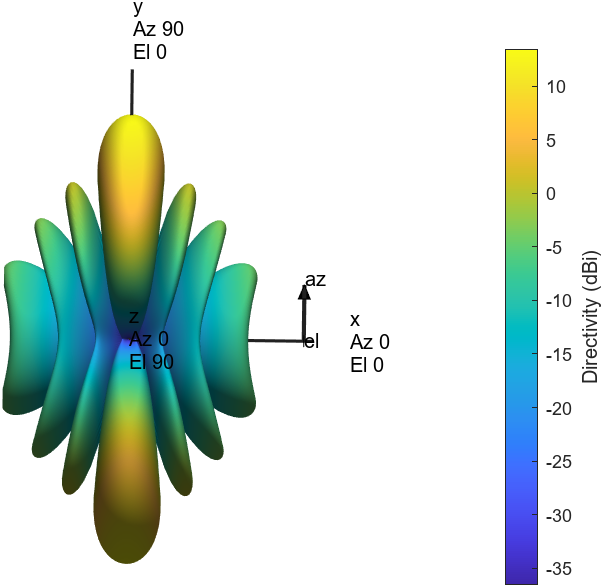
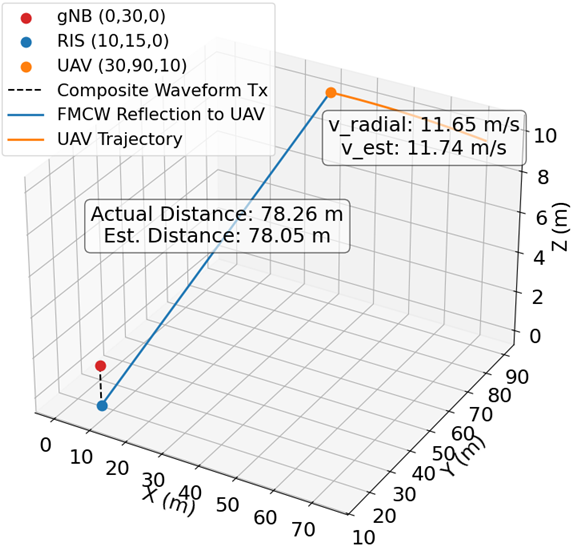
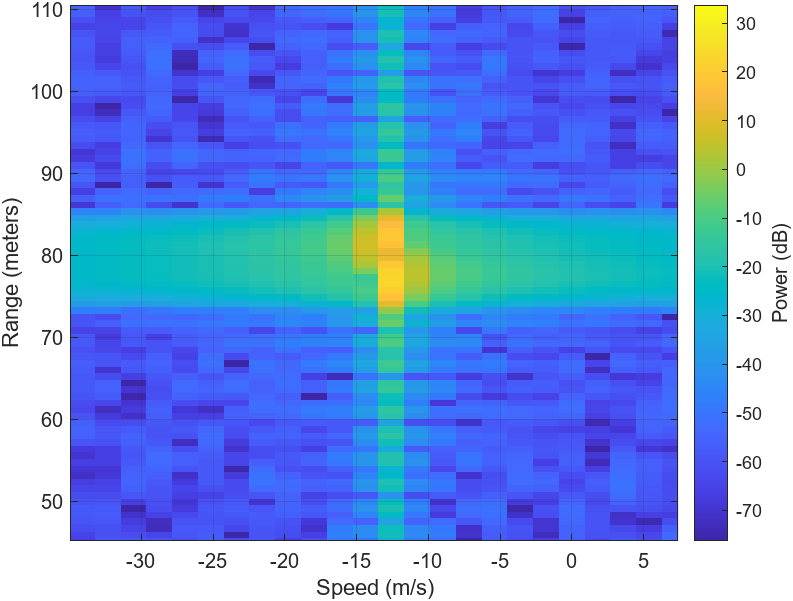
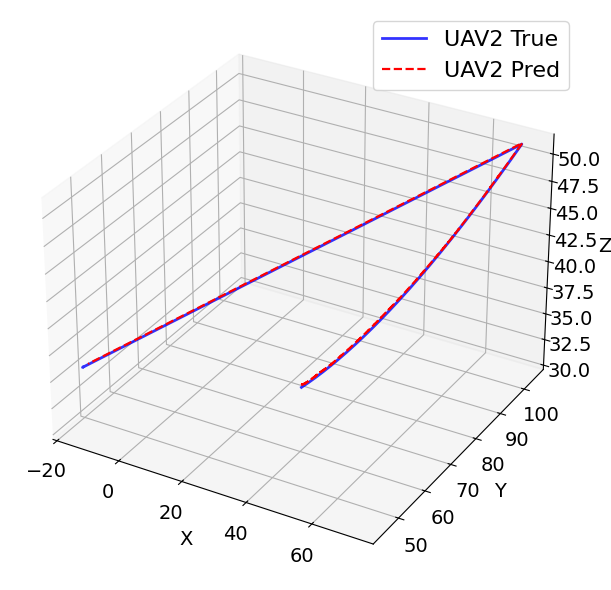
A RIS- and O-RAN–assisted Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) framework is presented for high-speed UAV detection and tracking in the 3.7 GHz band. The system integrates composite OFDM–FMCW waveforms, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS), and O-RAN distributed intelligence to enable scalable, low-latency, and adaptive sensing under spectrum-sharing constraints.
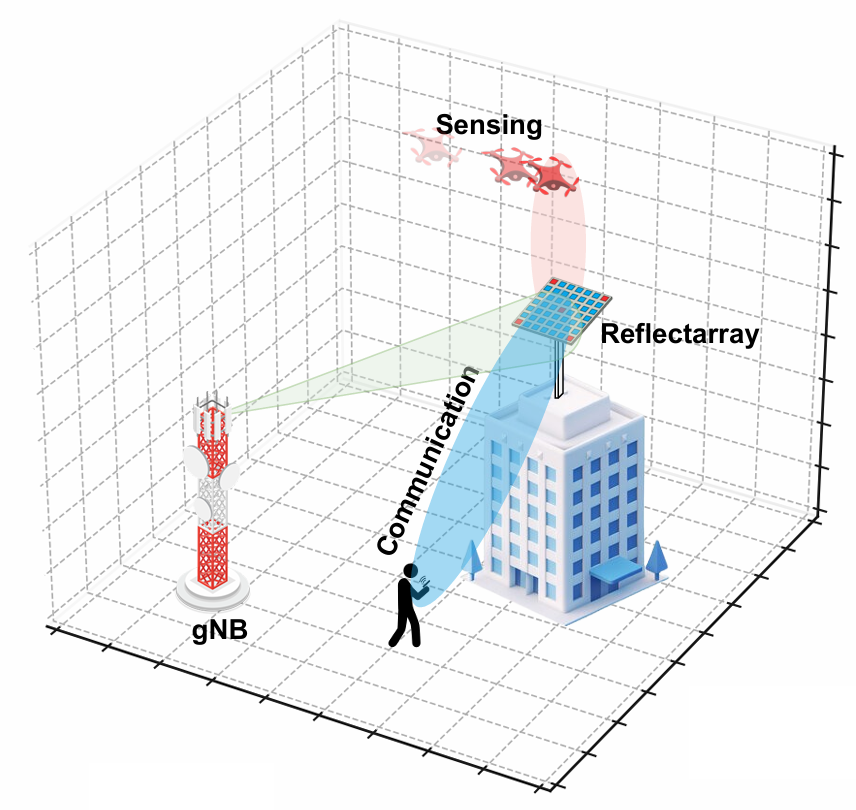
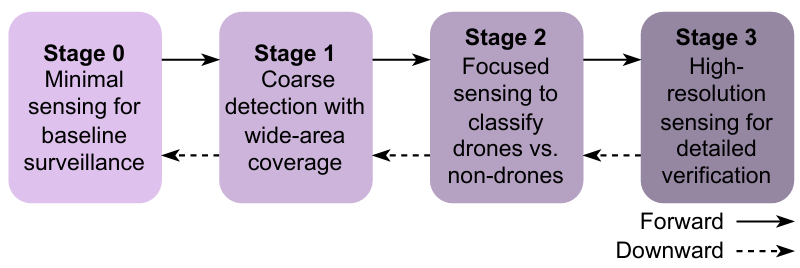
A four-stage state machine governs sensing resolution and resource allocation:
State transitions depend on detection confidence, SNR, QoS constraints, and resource availability.
Share
Latest Posts

The O-RAN/AI-RAN testbed integrates commercial servers, software-defined radios, and phased-array front-ends into a flexible, programmable wireless platform. It supports a disaggregated O-RAN architecture with virtualized O-CU/O-DU, O-RU, and near-/non-RT RIC, enabling real-time data collection, AI/ML-driven control, and over-the-air experimentation. This setup allows us to prototype intelligent and secure NextG radio access networks, validate ISAC waveforms, and rapidly iterate new algorithms from simulation to hardware.

A RIS- and O-RAN–assisted Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) framework is presented for high-speed UAV detection and tracking in the 3.7 GHz band. The system integrates composite OFDM–FMCW waveforms, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS), and O-RAN distributed intelligence to enable scalable, low-latency, and adaptive sensing under spectrum-sharing constraints.