We use cookies on this site to enhance your user experience
By clicking the Accept button, you agree to us doing so. More info on our cookie policy
We use cookies on this site to enhance your user experience
By clicking the Accept button, you agree to us doing so. More info on our cookie policy
Published: Aug 1, 2024
Authors:
Xiaochan (Luna) Xue
,
Saurabh Parkar
,
Shucheng Yu
,
Yao Zheng
ISAC Series
This post is part of a series all about ISAC.
Fundamental
Advanced
mmWave Breathing Pattern Detection
A lightweight Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) framework is presented for contactless respiration pattern recognition using a composite OFDM–FMCW waveform at 28 GHz mmWave. A narrowband FMCW radar signal is embedded into the OFDM guard band, enabling simultaneous high-resolution sensing and data communication without modifying the OFDM structure or requiring additional hardware.
Guard-band FMCW reuse preserves 5G NR spectral integrity
Robust respiration sensing under realistic body motion
Hardware validation on a mmWave USRP testbed
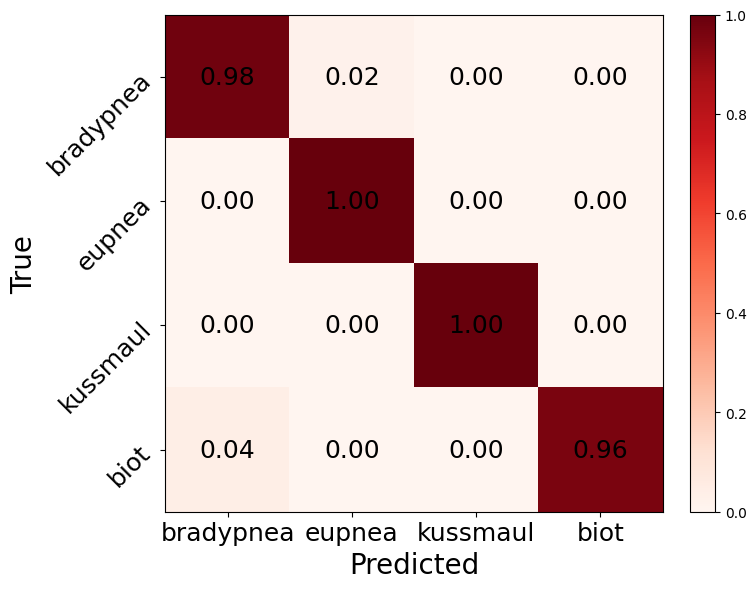
End-to-end AI pipeline achieving >98% classification accuracy
Narrowband FMCW chirps embedded into unused OFDM guard bands
No changes to OFDM modulation, framing, or scheduling
FMCW sweep bandwidth evaluated from 0.25–2 MHz
FMCW-to-OFDM power ratio systematically analyzed to balance sensing and communication
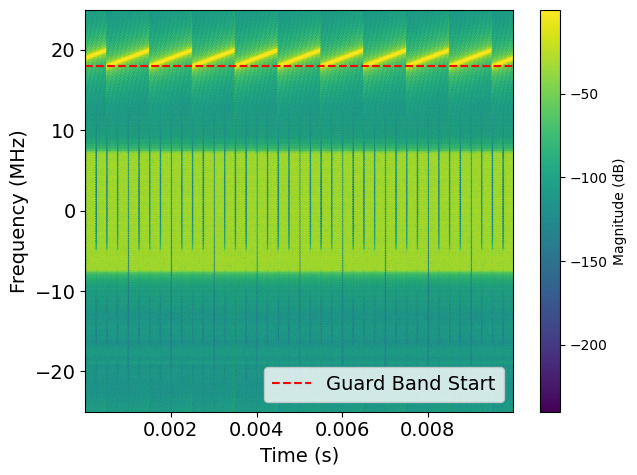
OFDM Mode
FMCW Mode
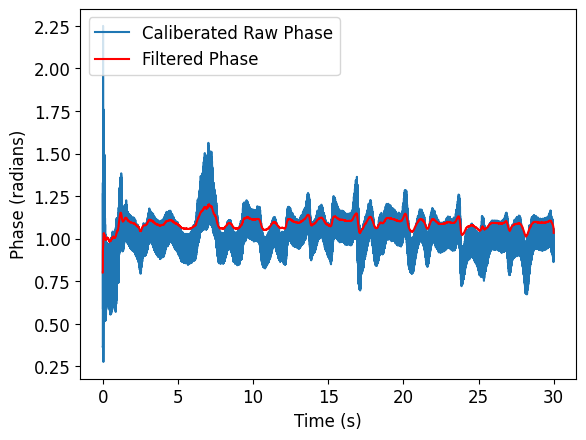
Dechirping and beat-frequency extraction
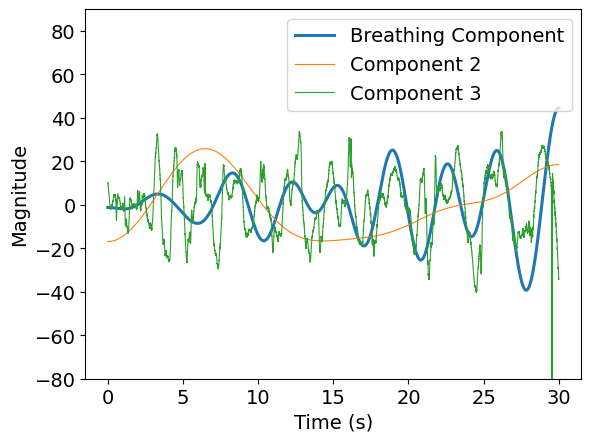
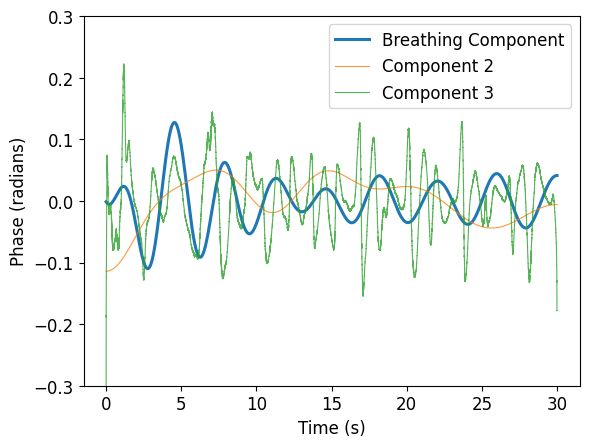
Range-bin selection for slow-time respiration signal
Drift suppression using detrend filtering
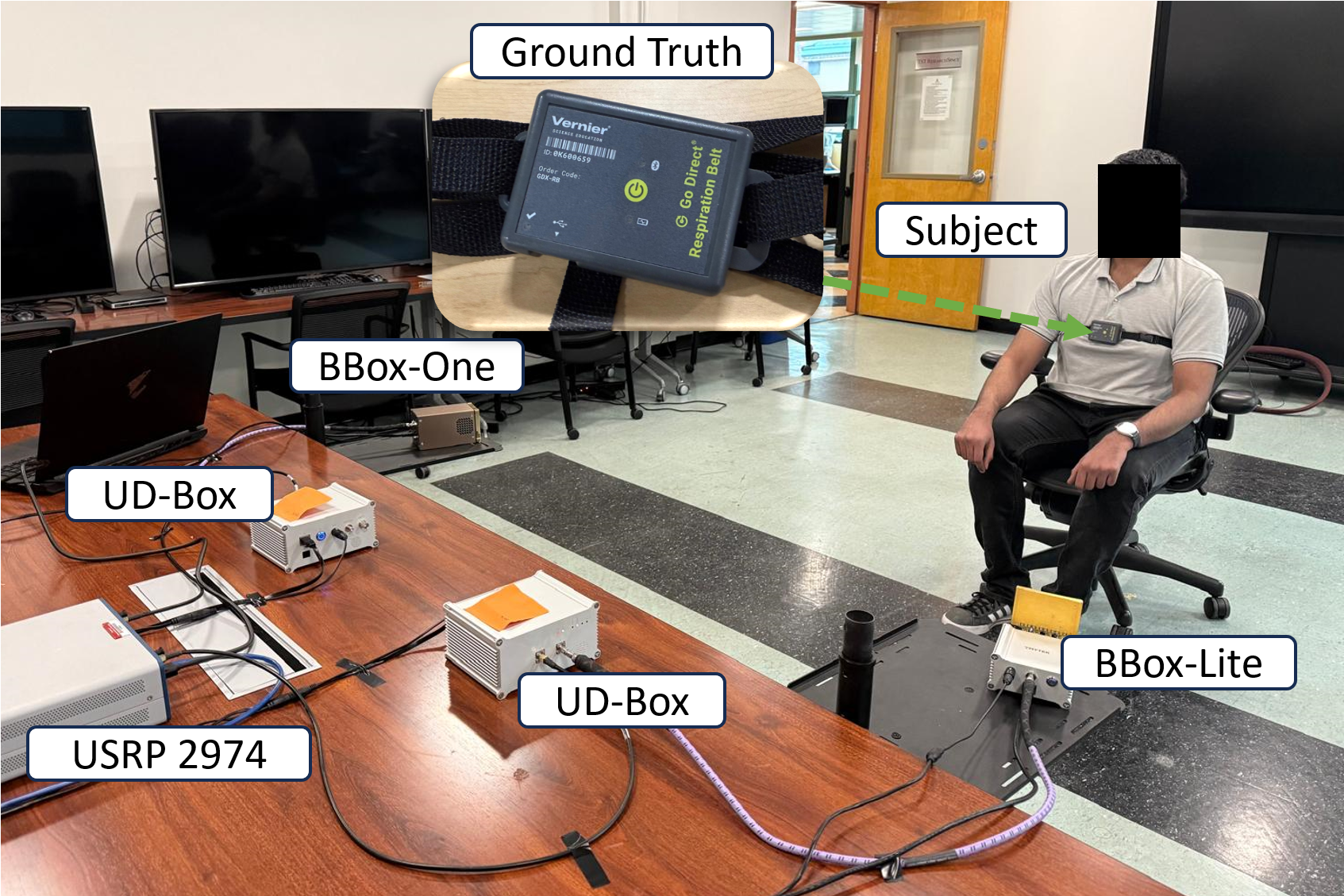
28 GHz mmWave testbed based on NI-USRP-2974
16-channel transmit and 4-channel receive phased arrays
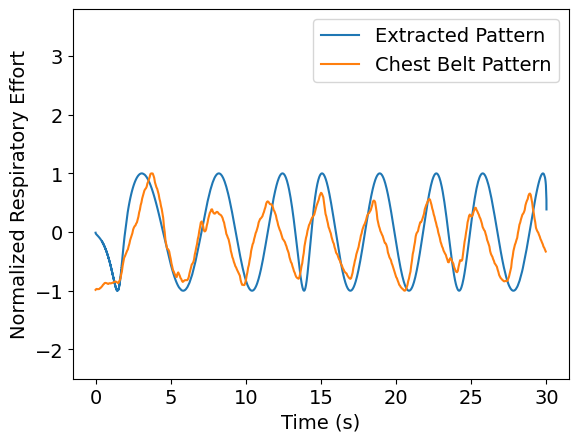
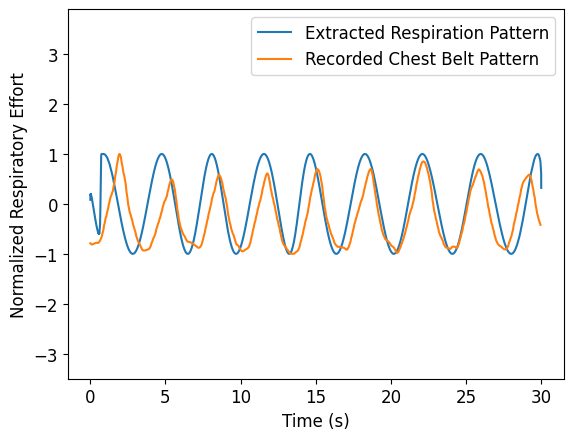
Input: normalized respiration waveforms
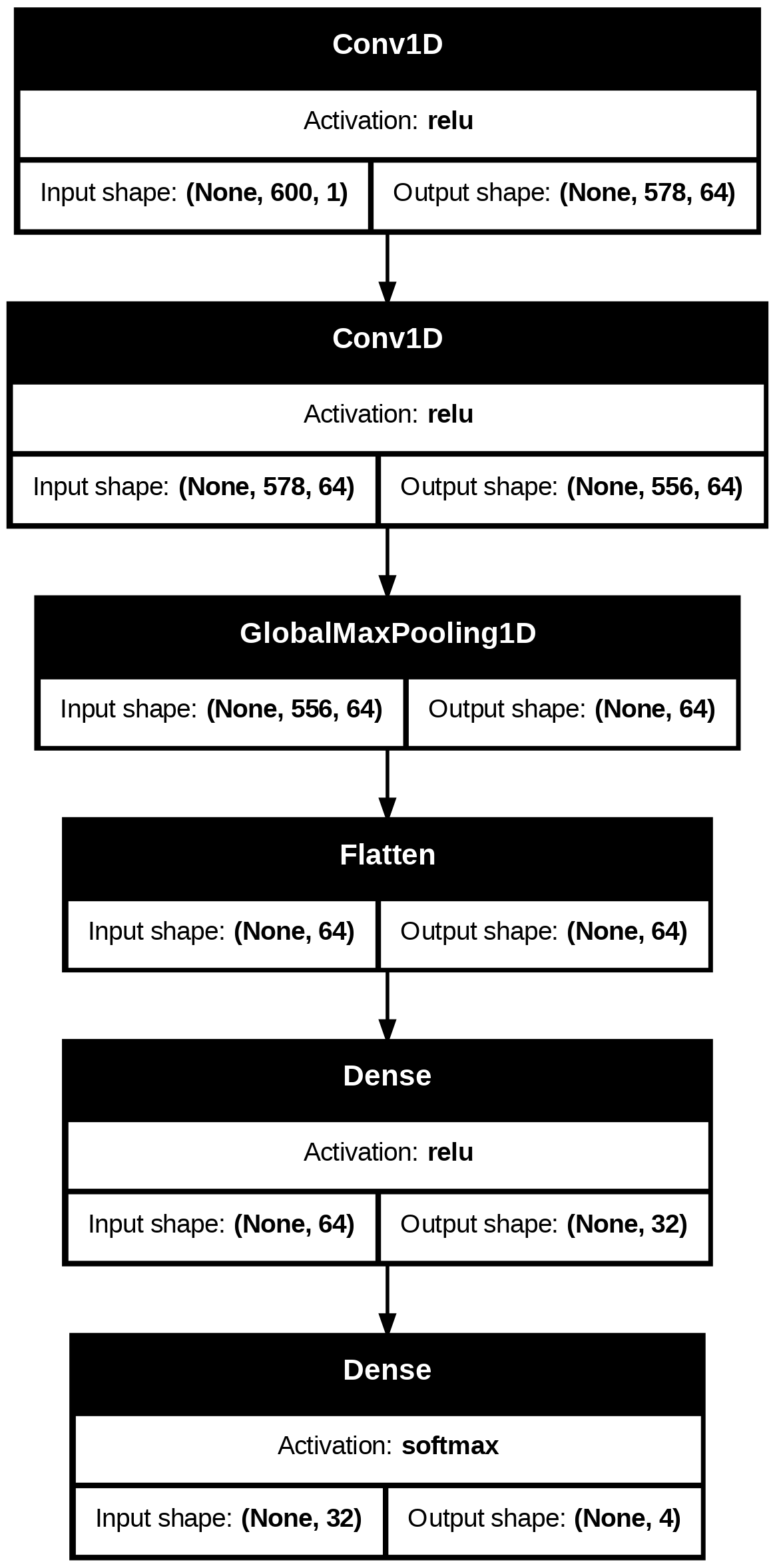
Model: lightweight 1D convolutional neural network (1D-CNN)
Two convolution layers followed by global max pooling
Output: multi-class respiration pattern prediction

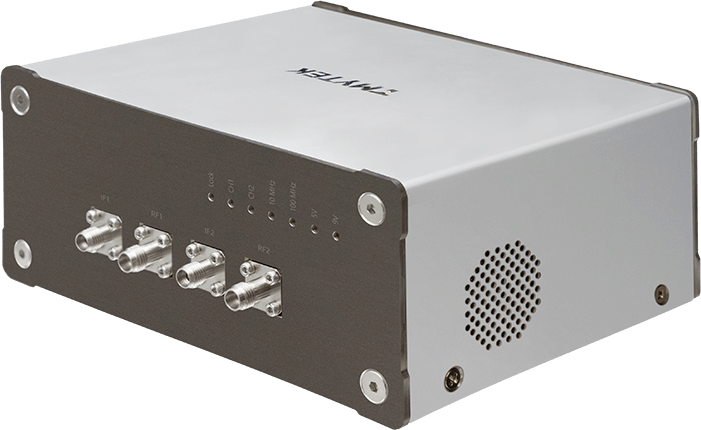
The USRP 2974 is a high-performance software-defined radio platform designed for advanced wireless research and development. It supports multiple frequency bands and provides flexible signal processing capabilities.
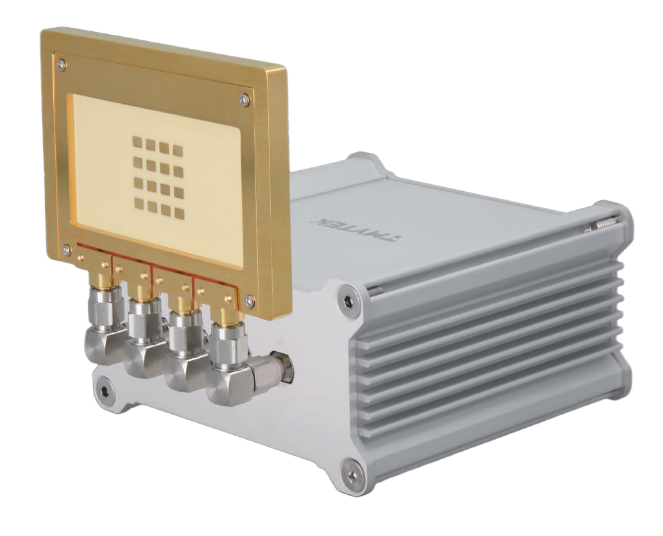

The X310 SDR platform offers robust performance for wireless communication research. It features wide frequency coverage and excellent signal quality for various experimental applications.

Our O-RAN testbed cluster provides a comprehensive environment for testing and validating Open Radio Access Network architectures and AI-driven network optimization.

Our O-RAN testbed cluster provides a comprehensive environment for testing and validating Open Radio Access Network architectures and AI-driven network optimization.
Share
Latest Posts

The O-RAN/AI-RAN testbed integrates commercial servers, software-defined radios, and phased-array front-ends into a flexible, programmable wireless platform. It supports a disaggregated O-RAN architecture with virtualized O-CU/O-DU, O-RU, and near-/non-RT RIC, enabling real-time data collection, AI/ML-driven control, and over-the-air experimentation. This setup allows us to prototype intelligent and secure NextG radio access networks, validate ISAC waveforms, and rapidly iterate new algorithms from simulation to hardware.
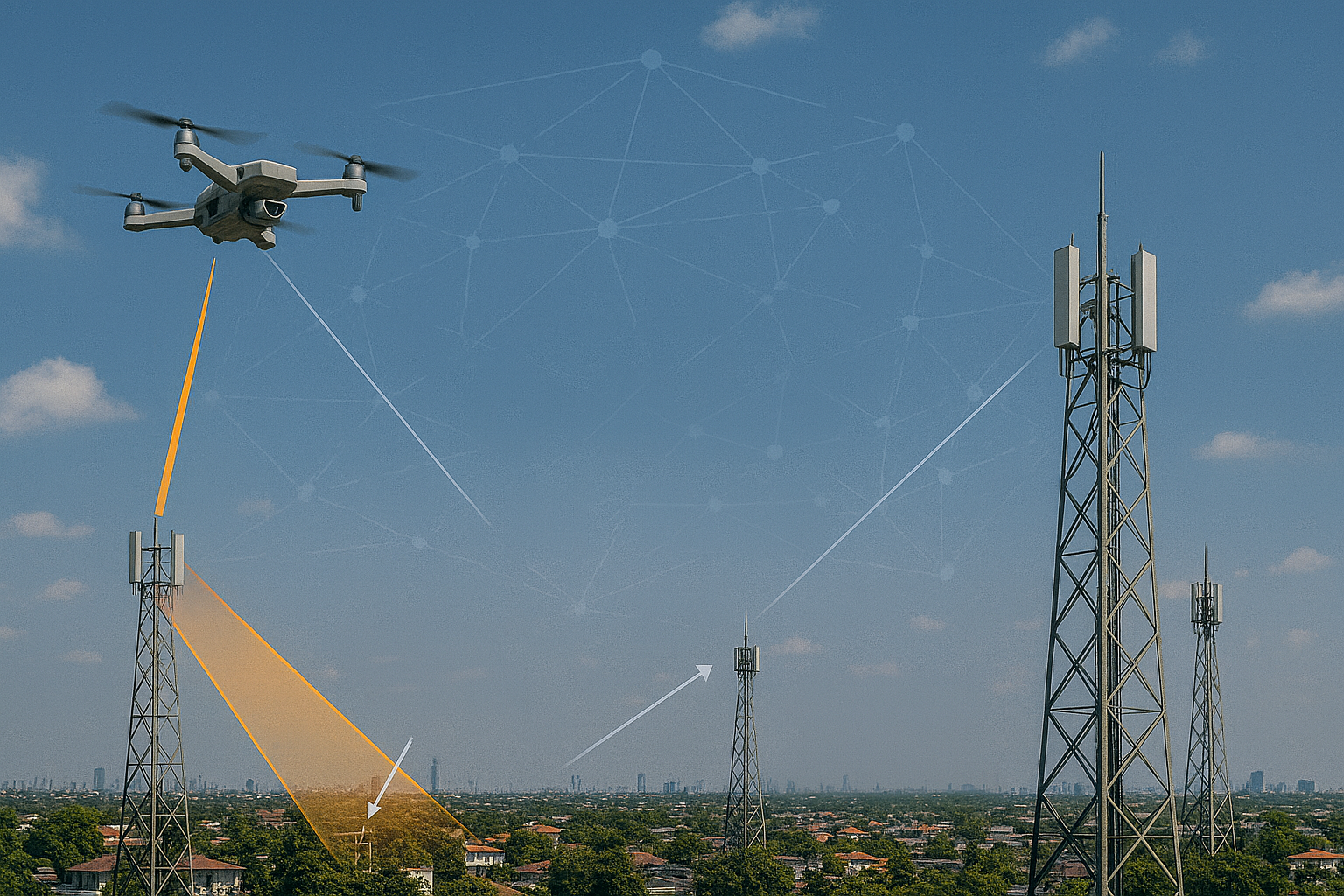

A RIS- and O-RAN–assisted Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) framework is presented for high-speed UAV detection and tracking in the 3.7 GHz band. The system integrates composite OFDM–FMCW waveforms, reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS), and O-RAN distributed intelligence to enable scalable, low-latency, and adaptive sensing under spectrum-sharing constraints.